News release
From:
Curtin researchers and international collaborators using advanced satellite imagery have discovered an ancient reef-like landform ‘hidden’ in plain view on the Nullarbor Plain, which has been preserved for millions of years since it first formed when the Plain was underwater.
Research author Dr Milo Barham, from the Timescales of Mineral Systems Group within Curtin’s School of Earth and Planetary Sciences said the finding further challenged the understanding that the Nullarbor Plain, which emerged from the ocean about 14 million years ago, was essentially flat and featureless.
“Unlike many parts of the world, large areas of the Nullarbor Plain have remained largely unchanged by weathering and erosion processes over millions of years, making it a unique geological canvas recording ancient history in remarkable ways,” Dr Barham said.
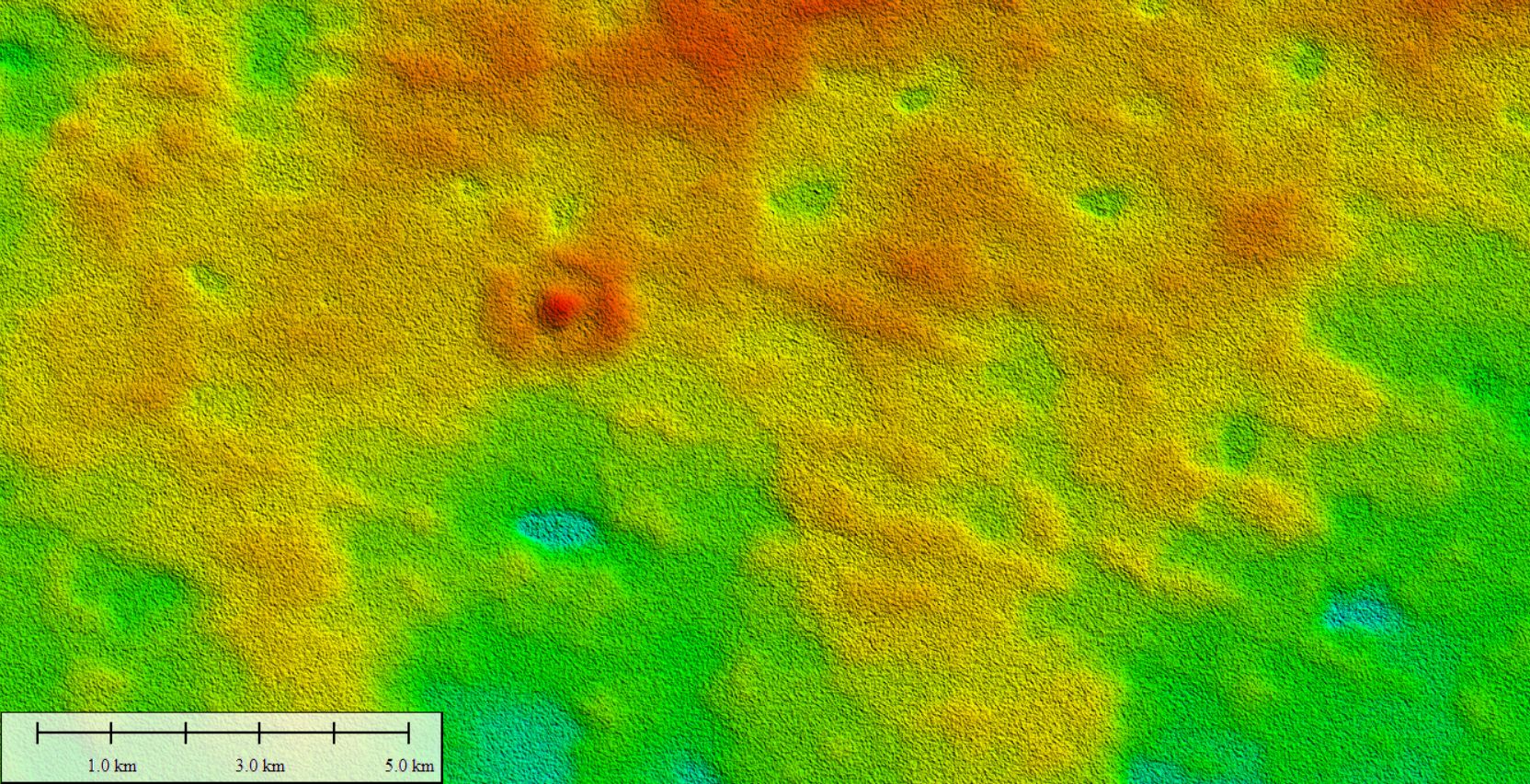
“Through high-resolution satellite imagery and fieldwork we have identified the clear remnant of an original sea-bed structure preserved for millions of years, which is the first of this kind of landform discovered on the Nullarbor Plain.
“The ring-shaped ‘hill’ cannot be explained by extra-terrestrial impact or any known deformation processes but preserves original microbial textures and features typically found in the modern Great Barrier Reef.”
Dr Barham said the discovery was due to greater access to new high-resolution satellite imagery, which revealed subtle features representing surprising histories of environmental evolution on the Nullarbor Plain.
“Evidence of the channels of long-vanished rivers, as well as sand dune systems imprinted directly into limestone, preserve an archive of ancient landscapes and even a record of the prevailing winds. And it is not only landscapes. Isolated cave shafts punctuating the Nullarbor Plain preserve mummified remains of Tasmanian tigers and complete skeletons of long-extinct wonders such as Thylacoleo, the marsupial lion,” Dr Barham said.
“At the surface, due to the relatively stable conditions, the Nullarbor Plain has preserved large quantities of meteorites, allowing us to peer back through time to the origins of our solar system.
“These features, in conjunction with the millions of years old landscape feature we have now identified, effectively make the Nullarbor Plain a land that time forgot and allow a fascinating deeper understanding of Earth’s history.”
Dr Barham is affiliated with The Institute for Geoscience Research (TIGeR), Curtin’s flagship Earth Sciences research institute.
Titled ‘Enigmatic annular landform on a Miocene planar karst surface, Nullarbor Plain, Australia’ and to be published in Earth Surface Processes And Landforms, the research was led by Dr Matej Lipar from the Anton Melik Geographical Institute at the Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts.



 Australia; International; WA
Australia; International; WA