News release
From:
Humans inherited their flexible joints from the earliest jawed fish
Synovial joints identified for the first time in multiple ancient fish lineages
The efficient architecture of our joints, which allows our skeletons to be flexible and sturdy, originated among our most ancient jawed fish ancestors, according to a study published February 25th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Neelima Sharma of the University of Chicago and colleagues.
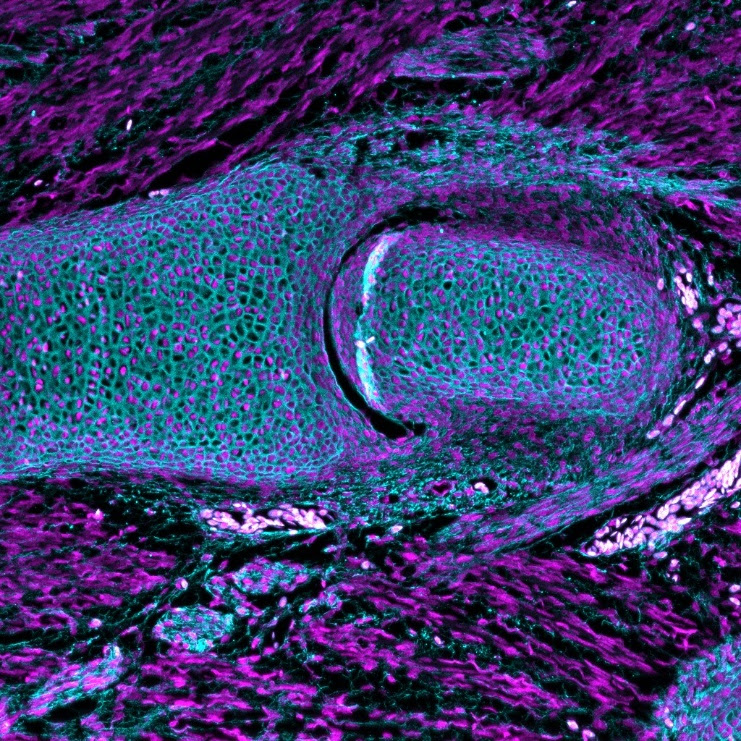
Synovial joints are a key feature of most vertebrate skeletons, providing more mobility and stability compared to other joint types. A synovial joint allows bones or cartilage to slide past each other with the aid of a lubricated cavity between them. These joints are present in land vertebrates and bony fish, suggesting this feature had evolved in the common ancestors of these groups, but it remains unclear when in early vertebrate evolution these joints originated.
In this study, Sharma and colleagues examined the anatomy and development of joints in members of two early-branching vertebrate lineages: one species of jawless fish, sea lampreys, and two species of cartilaginous fish, bamboo sharks and little skates. Analysis revealed cavitated joints in the cartilaginous fish, but not in lampreys. Additionally, the cartilaginous fish exhibited certain proteins and developmental processes that are shared with synovial joints of other vertebrates. Furthermore, the researchers employed CT-scans to identify a similar cavitated joint in the fossil fish Bothriolepis, the most ancient known synovial joint.
Altogether, these results show that synovial joints are shared across jawed fish, but apparently absent in jawless fish, indicating that these joints first evolved in the ancestors of jawed vertebrates. This study provides critical information for research into the origins of the skeletal architecture of vertebrates, including ourselves. The authors suggest that future steps might include analysis of joint morphology in other fossil fish lineages and further comparisons between joints of jawed and jawless vertebrates to uncover more details about early joint evolution.
The authors add, “The origin of mobile joints in our fish ancestors enabled them to move about and feed in new ways. This study shows that the developmental processes that are responsible for these joints arose deep within the fish evolutionary tree.”
Multimedia



 International
International