News release
From:
TB under the sea: A marine sponge microbe provides insights into the evolution of tuberculosis
The surprising discovery of a bacterium in a marine sponge from the Great Barrier Reef with striking similarity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the pathogen responsible for tuberculosis (TB), could unlock and inform future TB research and treatment strategies.
TB remains one of the world’s deadliest infectious diseases, yet the origins of M. tuberculosis are still not fully understood.
Often referred to as ‘chemical factories’, marine sponges are a valuable source of bioactive compounds with potent anticancer, antibacterial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. While studying a sponge specimen for its chemical-producing bacteria, researchers at the University of Queensland found a bacterium that puzzled them.
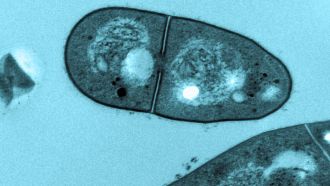
The sample was sent to the Doherty Institute, where the team conducted extensive analyses of the genes, proteins and lipids of M. spongiae. They discovered that it shares 80 per cent of its genetic material with M. tuberculosis, including some key genes associated with the bacteria’s ability to cause disease. However, the researchers found that, unlike M. tuberculosis, M. spongiae does not cause disease in mice, making it non-virulent.
The University of Melbourne’s Dr Sacha Pidot, a Laboratory Head at the Doherty Institute and co-lead author of the paper, said it was an exciting and important find.
“We were astounded to discover that this bacterium is a very close relative of M. tuberculosis,” said Dr Pidot.
“This finding provides new insights into the evolution of M. tuberculosis, suggesting that these pathogens may have originated from marine mycobacteria.”
The University of Melbourne’s Professor Tim Stinear, a Laboratory Head at the Doherty Institute and co-lead author of the paper, said that that this new knowledge is an important building block for future research.
“While there is more work to be done in this space, this discovery is a valuable piece in the puzzle of understanding how TB came to be such a serious disease,” said Professor Stinear.
“Our findings could help find weak links in M. tuberculosis to inform the development of new strategies such as vaccines to prevent and combat tuberculosis.”
---------------------
Additional information:
· Peer review: Pidot SJ, et al. Marine sponge microbe provides insights into evolution and virulence of the Tubercle bacillus. PLOS Pathogens (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012440
· Funding: This project was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), the Australian Research Council (ARC), University of Queensland, the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR).
· Collaboration: Authors who contributed were from Bio21 Institute, University of Queensland, Institut Pasteur, UK Health Security Agency, University of Otago and WEHI.
Multimedia



 Australia; New Zealand; VIC; QLD
Australia; New Zealand; VIC; QLD



