News release
From:
Association Between Melanoma Detected During Routine Skin Checks, Risk of Death
JAMA Dermatology
Original Investigation
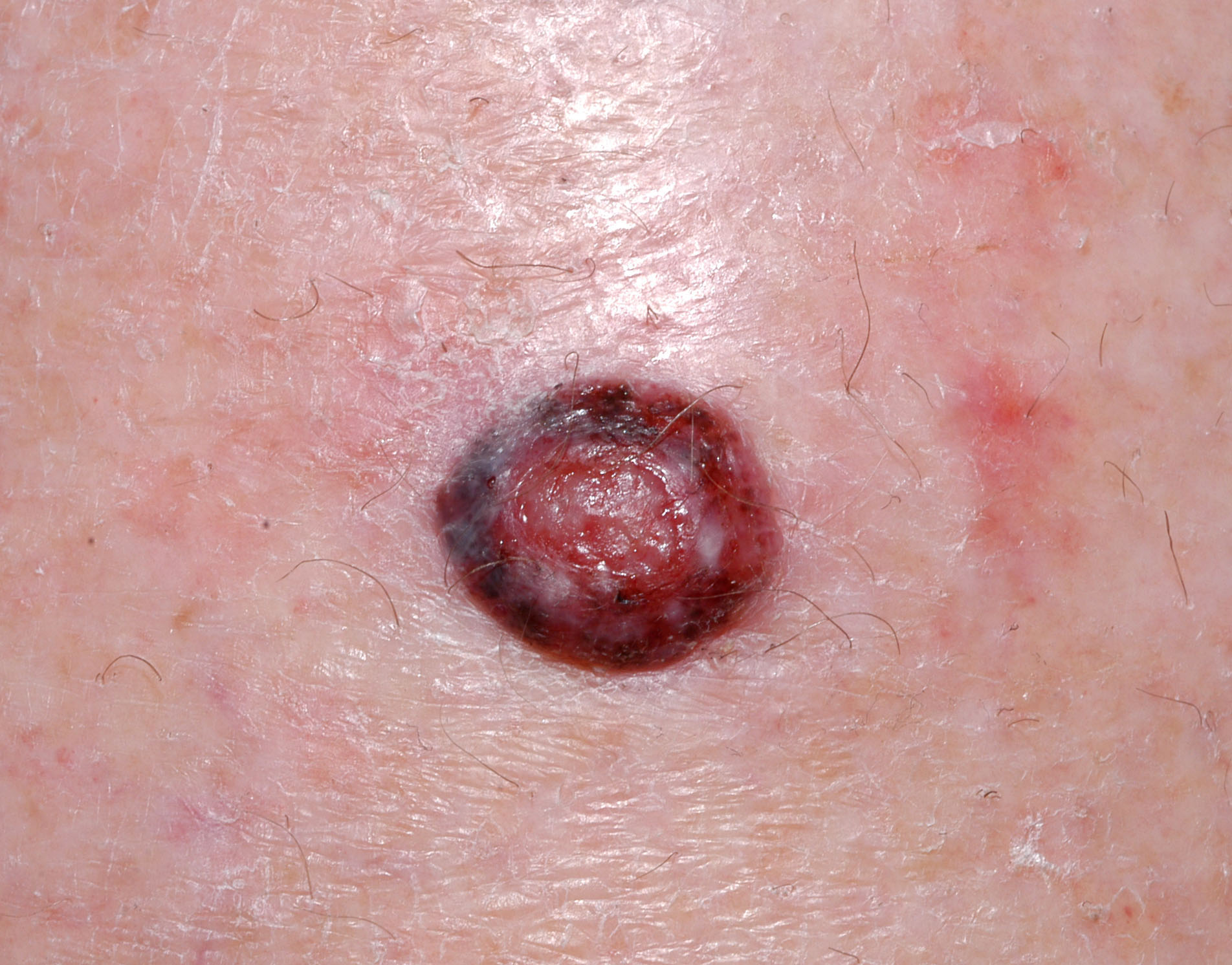
What The Study Did: Researchers found that melanomas diagnosed through routine skin checks were associated with a significantly lower all-cause risk of death but not melanoma-specific death in this study of 2,452 patients in Australia.
Authors: Anne E. Cust, Ph.D., of the University of Sydney, is the corresponding author.
Attachments
Note: Not all attachments are visible to the general public.
Research URLs will go live after the embargo ends.

Research
JAMA, Web page
Please link to the article in online versions of your report (the URL will go live after the embargo ends).
Journal/
conference:
JAMA Dermatology
Organisation/s:
The University of Sydney, The Kirby Institute for Infection and Immunity in Society, The University of New South Wales, The Westmead Institute for Medical Research, The University of Queensland, Australian National University
Funder:
Thisworkwas supported by the
Australian National Health and Medical Research
Council (grant No. 1135285 from the Centre of
Research Excellence in Melanoma and grant No.
1165936 from Project Grant); grant No. 05/POC/1-06
from the Cancer Institute New SouthWales; and the
New SouthWales State Government via a grant to
the New SouthWales Melanoma Network. Additional
financial and in-kind supportwas provided by the
Melanoma Institute Australia and the New South
Wales Melanoma Network; grant 1137127 from the
National Health and Medical Research Council Next
Generation Clinical Researchers Program Practitioner
Fellowship (Dr Soyer); a grant from the National
Health and Medical Research Council Practitioner
Fellowship (Dr Scolyer); investigator grant No.
1194703 from the National Health and Medical
Research Council (Dr Morton); a University of Sydney
Robinson Fellowship (Dr Morton); grant No. 1093017
from the National Health and Medical Research Council (Drs Scolyer, Mann, and Thompson); and a
Career Developmental Fellowship grant No. 1147843
from the National Health and Medical Research
Council (Dr Cust).



 Australia; NSW; QLD; ACT
Australia; NSW; QLD; ACT