News release
From:
Cancer drug conquers covid inflammation
A cancer drug could play an important role in limiting the damaging effects of lung disease in COVID- 19 patients, thanks to new research at Hudson Institute.
The body’s inflammatory response to infection is important in controlling viruses, such as SARS-CoV- 2, the virus that causes COVID-19, but when inflammation gets out of control the effects can be lethal.
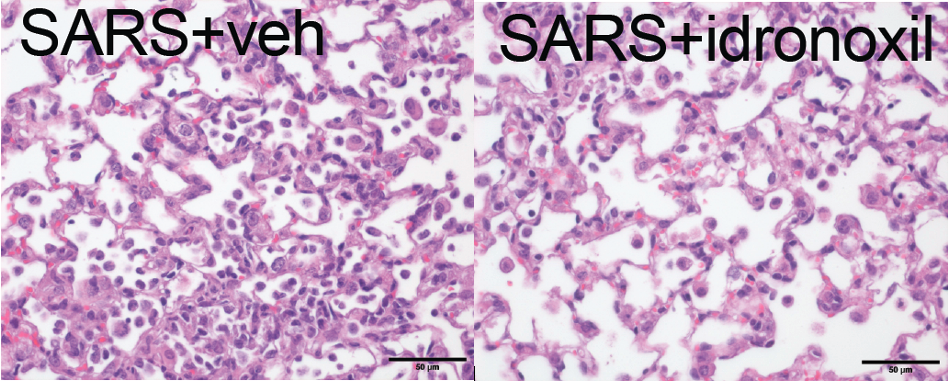
Now a team led by Associate Professor Michael Gantier has established that idronoxil, which was originally designed to treat cancers, could reduce the inflammation that occurs in response to COVID- 19.
His research is published in the latest edition of Nature Communications.
Immune system overdrive
“Early in the COVID-19 pandemic we realised that uncontrolled inflammation was one of the major life-threatening aspects of the infection, but we didn’t know exactly how this inflammation occurred,” A/Prof Gantier said.
“While fighting the infection caused by SARS-CoV-2, our immune system can sometimes go in overdrive - i.e. when the off-switch does not work.
“The problem is that blocking the immune response too early can help the virus better replicate and do more damage.
“We’ve now shown that therapeutic targeting of a single protein activated by several inflammatory pathways can help limit the bad inflammation, without increasing viral replication in the lung,” he said.
“This led us to discover that idronoxil administered 3 days after infection could reduce the inflammation resulting from SARS-CoV-2 infection in a pre-clinical model of the severe disease.”
“In other words, we can let the body’s inflammatory response go to work without going too far – we’ve restored the off-switch.”
This preclinical work, with PhD student Tomalika Ullah, was conducted in parallel with an early clinical trial on moderate SARS-CoV-2 patients in 2021, which demonstrated that idronoxil was safe in this disease context.
Potential to treat emerging viruses
A/Prof Gantier believes idronoxil or its potential derivatives could be used to help treat viral induced lung hyperinflammation driven by emerging viruses – in other words, they could be the remedies that were so desperately needed during the pandemic.
As COVID-19 illustrated, our hospitals were ill-prepared to fight an influx of patients with respiratory distress, and more drugs are clearly needed to prevent this from happening again.
A/Prof Gantier and his team of academic and industry collaborators are currently developing idronoxil derivatives with enhanced anti-inflammatory activities, leveraging $1.45M funding support from the Victorian Government through the COVID-19 Treatments Medical Research Fund.
Collaborators on this project include Monash University, UTS and Centenary Institute, ANU, St. Vincent’s Institute of Medical Research, UNSW, University of Adelaide, Francis Crick Institute and Noxopharm Limited.
Facts
- COVID-19 has highlighted how damaging out-of-control inflammation can be.
- Patients with severe COVID-19 develop out-of-control inflammation as their bodies try to fight the virus.
- This triggers a severe hyper-inflammatory response leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and organ failure.
- Restricting this inflammatory response could help save lives.
Multimedia



 Australia; NSW; VIC; SA; ACT
Australia; NSW; VIC; SA; ACT