Media release
From:
Hate speech on X found to have increased under Elon Musk’s leadership
New findings contrast with X’s claims of reduced exposure to hate speech and bot activity
A new analysis suggests that the rate of hate speech on X was about 50 percent higher for several months after Elon Musk purchased the social media platform than in prior months, and the amount of bot and bot-like accounts did not decline. Daniel Hickey of the University of California, Berkeley, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on February 12, 2025.
Prior research has linked online hate speech to offline hate crimes, and bots and bot-like accounts can promote misinformation and spam that could cause harm, such as by contributing to scams, interfering with real-world elections, or hindering public health campaigns. Earlier studies have shown that, immediately after Musk purchased X, then known as Twitter, and became its CEO on October 27, 2022, hate speech increased on the platform, and the amount of bot or other inauthentic accounts did not decrease—despite Musk’s pledge to reduce bot activity.
However, it has been unclear whether such trends endured throughout the rest of Musk’s tenure as CEO, until June 2023. To address this gap, Hickey and colleagues employed previously developed methods to measure English-language hate speech and inauthentic activity on X during that period.
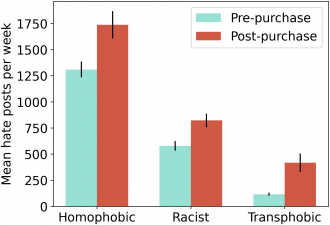
The analysis showed that a spike in hate speech that occurred just before Musk purchased X continued through May 2023. The weekly rate of hate speech was about 50 percent higher than in months prior to the purchase, including increased use of specific homophobic, transphobic, and racist slurs. The average number of “likes” on hate posts increased by 70%, suggesting that more people were exposed to hate speech on X. Meanwhile, the presence of bot accounts and other inauthentic accounts did not decrease and may in fact have increased.
These findings do not support public claims from X that exposure to hate speech decreased after Musk’s purchase.
The researchers note that, because information on specific internal changes at X is limited, they cannot draw firm conclusions about a cause-effect relationship between Musk’s purchase of X and their findings. Nonetheless, they express concern about the safety of online platforms and call for increased moderation on X as well as further research to illuminate activity across social media platforms.
The authors add: “The policies to reduce exposure to harmful content appear not to be sufficiently effective.”
Multimedia



 International
International



