News release
From:
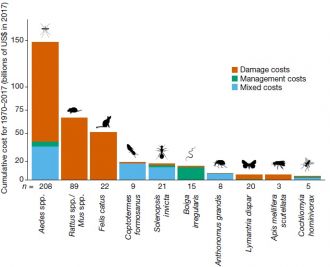
A new analysis has revealed the stark US$1.28 trillion economic damage caused by the world’s invasive species over the past half century — with a group of global experts warning damage and management costs will soar unless biodiversity agencies can improve prevention and control of biological invasions.
The research, published in leading global scientific journal Nature, shows invasive species have damaged crop yields, critical national infrastructure, human health and diverted billions in taxpayer dollars annually, but too little is being done because the impact isn’t well-recognised by decision-makers and the public.
Biological invasions take place when species of animals, plants and pathogens are deliberately or accidentally introduced in regions not previously occupied by these species.
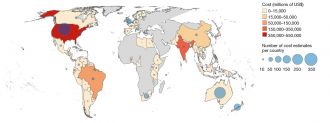
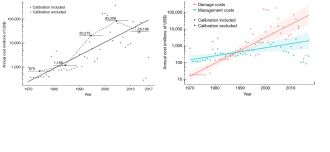
The researchers analysed thousands of costs estimates and used models to estimate the annual losses of US$26.8 billion between 1970–2017 caused by invasive species.
They highlight the importance of addressing rapidly rising expenses of up to US$162 billion in 2017, which are set to rise into the trillions in coming years because of the increase of biological invasions. Emerging diseases such as COVID-19 were not included in these already staggering amounts.
Lead author Dr Christophe Diagne of University Paris-Saclay says he and his colleagues have created a reliable, standardized catalogue of the economic costs caused by biological invasions to help clarify the importance of effective management policies going forward.
“This trillion-dollar bill doesn’t show any sign of slowing down, with a consistent threefold increase per decade.”
“Our annual global estimates signify the huge economic burden, with the average cost exceeding the gross domestic product of 50 countries on the African continent in 2017, and it’s more than 20 times higher than the total funds available for the World Health Organization and UN combined.”
Professor Corey Bradshaw of Flinders University says biological invasions are increasingly exacerbated by globalization and climate change, but no government is prepared to manage the crisis without substantial costs.
“We found that costs roughly doubled every 6 years, a pattern that mimics the continuous increase in the number of alien species worldwide.”
Despite their devastating ecological impacts - they are the second cause of species extinction - the public and decision makers remain largely unaware of the threats of biological invasions. With this study, we hoped that the realization of the significant economic costs they also cause would raise awareness» said Franck Courchamp, Project Director.
“The global costs of invasive alien species are so massive that we spent months verifying our models and this overall estimate, to insure we were not exaggerating” explains Christophe Diagne, the first author of the article. “As it turns out, our very conservative approach is in fact a massive underestimation of the actual economic costs".
“The trend can be explained by a combination of factors: the ongoing intensification of global trade and transport creates many more opportunities for invasions; the growing ‘land take’ of the planet surface, for example, expansion of agriculture and infrastructure, makes our societies sensitive to impacts from these invasions.”
The researchers say biological invasions should become a major factor when deciding transnational projects.
One of the most contemporary examples is the ambitious Belt and Road Initiative by China that will open avenues for the introduction of new species around the world.
The team of multidisciplinary researchers from Université Paris-Saclay, Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle of Paris, Université de Montpellier, University of South Bohemia, and Flinders University warn the costs in both developed and developing economies are soaring, and will continue to do so unless governments coordinate effective international policies to reduce the risks.
“That’s why we’re calling for international policy agreements that aim to reduce the burden of invasive species.”, adds Professor Bradshaw.
The Nature paper by Diagne C, Leroy B, Vaissière A-C, Gozlan RE, Roiz D, Jarić I, Salles JM, Bradshaw CJA & Courchamp F (2021) is ‘High and rising economic costs of biological invasions worldwide’. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03405-6
Multimedia



 Australia; SA
Australia; SA



