News release
From:
University of Queensland researchers have found a way to reverse a cellular process triggered by COVID-19 that contributes to premature ageing of the brain.
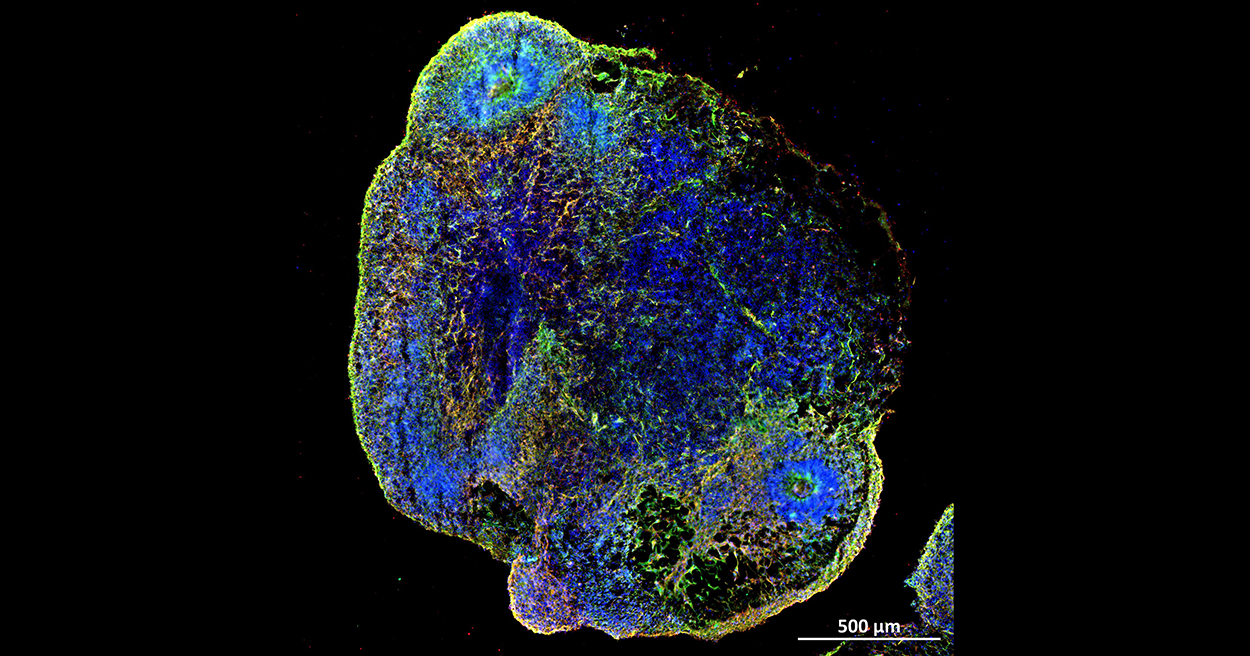
Dr Julio Aguado and a team from UQ’s Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology used synthetic brain organoid models, grown in a laboratory from human stem cells, to study the effect of different SARS-COV-2 variants on brain tissue.
“We found COVID-19 accelerates the presence of ‘zombie’ or senescent cells, which accumulate naturally and gradually in the brain as we get older,” Dr Aguado said.
“Senescent cells are known to drive tissue inflammation and degeneration, leaving patients exposed to cognitive impairments like brain fog and memory loss.”
Dr Aguado said confirmation that COVID-19 was a catalyst for this premature ageing prompted an attempt to reset the biological brain clock.
“We used the brain organoids to screen a range of therapeutics, looking for any capable of removing those senescent cells,” he said.
The researchers found four drugs that selectively eliminated the cells caused by COVID-19 – navitoclax, ABT-737, fisetin, and a cocktail of dasatinib plus quercetin (D+Q)
Dr Aguado said the drugs rejuvenated the brain and decreased the chance of neurodegenerative symptoms in the organoids, as well as in a mouse model infected with COVID-19.
“More research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms at play, but this study marks a significant step forward in our knowledge of the intricate relationship between viral infections, ageing and neurological well-being,” he said.
“Long term, we can expect widespread use of these drugs to treat persistent post-acute infection syndromes caused by viral infections like COVID-19.”
AIBN organoid expert Professor Ernst Wolvetang said human stem cell-derived brain organoids allow researchers to carry out experiments that would be ethically and practically difficult in human subjects.
“Our study beautifully demonstrates how human brain models can accelerate the pre-clinical screening of therapeutics – while also moving towards animal-free testing - with potentially global impacts,” Professor Wolvetang said.
“This same method of drug screening could also help Alzheimer’s research and a whole host of neurodegenerative diseases where senescence is a driver.”
The study was carried out with the support of researchers from Australia, the UK, the US, Chile, Germany, and Russia.
Multimedia





 Australia; QLD; SA
Australia; QLD; SA