News release
From:
“Movies” with color and music visualize brain activity data in beautiful detail
Novel toolkit translates neuroimaging data into audiovisual formats to aid interpretation
Complex neuroimaging data can be explored through translation into an audiovisual format – a video with accompanying musical soundtrack – to help interpret what happens in the brain when performing certain behaviors. David Thibodeaux and colleagues at Columbia University, US, present this technique in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on February 21, 2024. Examples of these beautiful “brain movies” are included below.
Recent technological advances have made it possible for multiple components of activity in the awake brain to be recorded in real time. Scientists can now observe, for instance, what happens in a mouse’s brain when it performs specific behaviors or receives a certain stimulus. However, such research produces large quantities of data that can be difficult to intuitively explore to gain insights into the biological mechanisms behind brain activity patterns.
Prior research has shown that some brain imaging data can be translated into audible representations. Building on such approaches, Thibodeaux and colleagues developed a flexible toolkit that enables translation of different types of brain imaging data—and accompanying video recordings of lab animal behavior—into audiovisual representations.
The researchers then demonstrated the new technique in three different experimental settings, showing how audiovisual representations can be prepared with data from various brain imaging approaches, including 2D wide-field optical mapping (WFOM) and 3D swept confocally aligned planar excitation (SCAPE) microscopy.
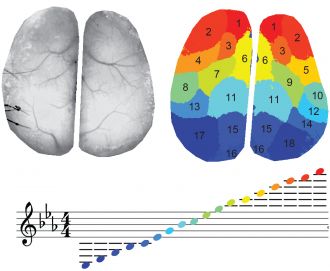
The toolkit was applied to previously-collected WFOM data that detected both neural activity and brain blood flow changes in mice engaging in different behaviors, such as running or grooming. Neuronal data was represented by piano sounds that struck in time with spikes in brain activity, with the volume of each note indicating magnitude of activity and its pitch indicating the location in the brain where the activity occurred. Meanwhile, blood flow data were represented by violin sounds. The piano and violin sounds, played in real time, demonstrate the coupled relationship between neuronal activity and blood flow. Viewed alongside a video of the mouse, a viewer can discern which patterns of brain activity corresponded to different behaviors.
The authors note that their toolkit is not a substitute for quantitative analysis of neuroimaging data. Nonetheless, it could help scientists screen large datasets for patterns that might otherwise have gone unnoticed and are worth further analysis.
The authors add: “Listening to and seeing representations of [brain activity] data is an immersive experience that can tap into this capacity of ours to recognize and interpret patterns (consider the online security feature that asks you to “select traffic lights in this image” – a challenge beyond most computers, but trivial for our brains)...[It] is almost impossible to watch and focus on both the time-varying [brain activity] data and the behavior video at the same time, our eyes will need to flick back and forth to see things that happen together. You generally need to continually replay clips over and over to be able to figure out what happened at a particular moment. Having an auditory representation of the data makes it much simpler to see (and hear) when things happen at the exact same time.”
Multimedia



 International
International


