News release
From:
Climate change: The Arctic is warming nearly four times faster than the rest of the world *IMAGES*
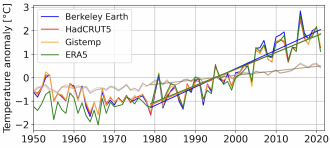
The Arctic is warming faster than previously thought, compared to the global average, reports an article published online in Communications Earth & Environment. This accelerated Arctic warming suggests that the region is more sensitive to global warming than current estimates.
Previous studies have reported the Arctic to be warming at, on average, between double and triple the rate of the rest of the globe — a phenomenon called Arctic amplification.
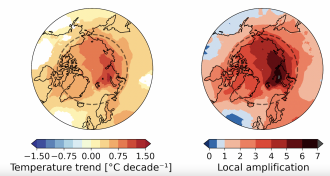
Mika Rantanen and colleagues analysed observational data from the Arctic Circle between 1979 and 2021 and estimated that a large proportion of the Arctic Ocean warmed at a rate of 0.75°C per decade during this period, at least four times faster than the global average. In the Eurasian sector of the Arctic Ocean, near the Svalbard and Novaya Zemlya archipelagos, warming was found to be as high as 1.25°C per decade; seven times faster than the rest of the world. The authors suggest that Arctic amplification is intensifying over time due to increased sea ice loss.
The authors suggest that climate model predictions may have generally underestimated Arctic amplification between 1979 and 2021, and call for more detailed investigations of mechanisms behind Arctic amplification and their representation in climate models.
Multimedia




 International
International



