News release
From:
Combo Therapy Halts Colon Cancer Growth
A colon cancer research breakthrough at Hudson Institute has shown that combining two types of drugs targeting gene expression stops cancer proliferation.
Australia has one of the highest rates of colon cancer (also known as bowel cancer or colorectal cancer) in the world - 1 in 13 Australians will develop the disease in their lifetime – and it is the nation’s second deadliest cancer.
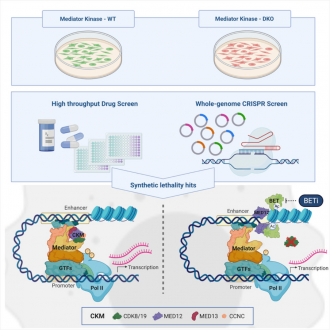
Now pre-clinical research has shown that disabling two proteins together robs cancer cells of their ability to express genes necessary for their growth and spread.
How the transcription machinery works
The research, to be published in the journal Molecular Cell this week, marks a significant step in the understanding of how the transcription machinery process works in cancer cells.
Associate Professor Ron Firestein is the Head of the Cancer Centre at the Hudson Institute of Medical Research.
He believes this latest finding could have far-reaching impacts for not just bowel cancer but other cancer types as well.
“In total, this work has found the ‘two brake pads’ that when pressed together stops cancer gene expression and growth,” A Prof Firestein said.
“Importantly, the two drugs we tested together are already in clinical and pre-clinical development, offering an expedient path for translating these findings to human patients.”
“This research goes beyond bowel cancer and shows that cancer cells are fundamentally evasive and utilise multiple paths to express the genes that they require for growth and spread.
Two classes of proteins work together
“Specifically, we show that two classes of proteins, CDK8/19 and BET proteins, work together to drive gene expression in cancer cells.
“Remarkably, when cancer cells were treated with inhibitors targeting both proteins, they could no longer express the genes required for malignancy.
Funders
NHMRC
Collaborators
Monash Health
Monash University
Available for interview:
· Associate Professor Ron Firestein
· Dr Claire Sun
· 2 bowel cancer patients
Photos can be organised
Multimedia



 Australia
Australia


