News release
From:
Sophisticated CT scanning of the cranium of a Queensland fish fossil has given new insights to explain how fish first left the water to invade land about 370 million years ago.
Supported by the Australian Research Council and international experts, the new research led by Flinders University palaeontologists studied Cladarosymblema narrienense, a 330 million-year-old fish from the Carboniferous Period found in Queensland, which is an ancestor of the first land animals or four-limbed vertebrate tetrapods.
Cladarosymblema is a type of 'megalichthyid' fish, a group which existed from the Devonian-to-Permian periods, typically living in freshwater environments, and they were large, predatory animals. Through scanning the fossil, they found evidence this fish had a brain similar to its eventual terrestrial descendants, compared to the brains of other fishes which remained living in water.
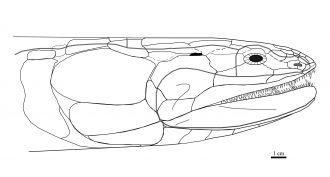
“This fish from Queensland is one of the best preserved of its kind in the entire world, in perfect 3D shape, which is why we chose to work on it,” says Professor John Long, Strategic Professor in Palaeontology at Flinders University.
While this fish was first described in 1995, by Professor Long and others who had earlier explored and excavated the Queensland fossil site, parts of its anatomy have remained unknown – although using Australia’s largest cabinet CT scanner, located at Flinders University’s Tonsley campus, as well as the Australian Synchrotron in Melbourne, has allowed researchers to unlock new data from this fossil.
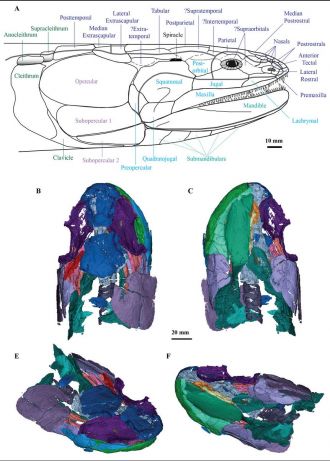
New information obtained from often unseen internal bones has been revealed in these scans - particularly in the gill arch skeleton, the shoulder girdle and the palate bones (the upper mouth roof area).
“This helps us to understand the functional morphology and relationships of Cladarosymblema,” says Dr Alice Clement, lead author of the new paper and part of the Flinders Palaeontology Group.
“Additionally, a cranial endocast (mould of the internal cavity of this fish’s unusually large skull) gives clues as to the shape of the brain of this animal. The area for the pituitary gland (so-called the ‘master gland’) is relatively large, suggesting a significant role in regulating various important endocrine glands.”
The research – ‘A fresh look at Cladarosymblema narrienense, a tetrapodomorph fish (Sarcopterygii: Megalichthyidae) from the Carboniferous of Australia, illuminated via X-ray tomography’, by Alice Clement, Richard Cloutier, Jing Lu, Egon Perilli, Anton Maksimenko and John Long - has been published in PeerJ (DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12597).
The researchers conducted a phylogenetic analysis, which confirms that the megalichthyid fish form a monophyletic group (a natural clade). Cladarosymblema is found to be one of the more derived members of the group.
(This is the first publication to feature specimens scanned by the new CT scanner at Flinders University)
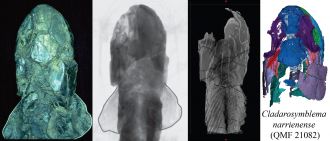
• The attached image has 4 panels showing: a photo of the specimen, a radiograph of the specimen, a tomogram (slice) of the specimen, and a 3D model of the specimen.
• Animations of the 3D models and renders can be accessed here.
Multimedia




 Australia; VIC; SA
Australia; VIC; SA


