Media release
From: University of South AustraliaUniversity of South Australia scientists have made a surprising discovery in the origins of an antibiotic-resistant gene previously thought to have been confined to Adelaide.
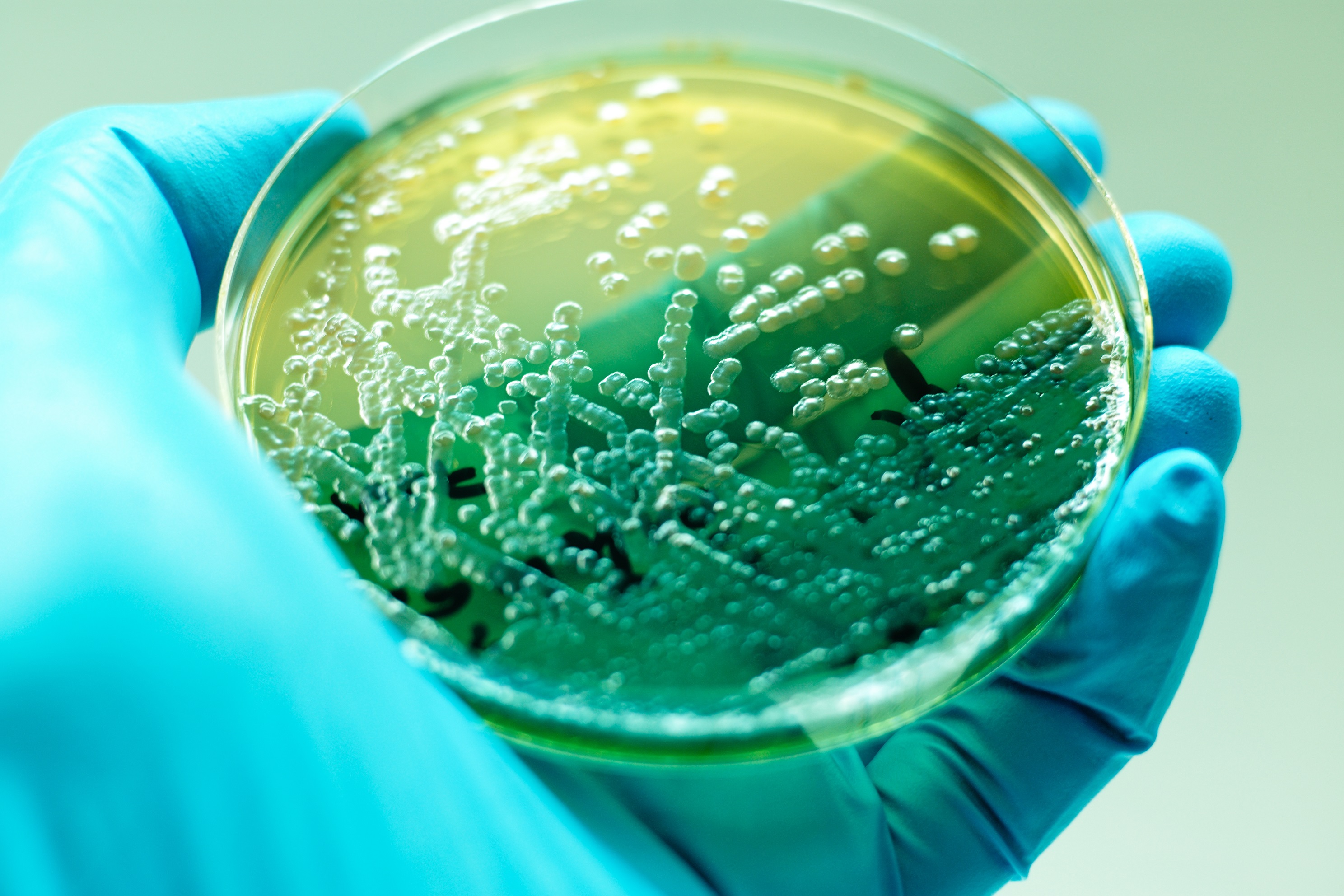
The gene, first detected in Adelaide in 2006, is carried by the nasty bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, an organism responsible for thousands of deaths among immunocompromised, surgical and burns patients due to its resistance to last resort antibiotics.
This gene makes infections resistant to the most potent antibiotics used in medicine – imipenem and meropenem. Antibiotic resistant P. aeruginosa is now listed by the World Health Organization as a “critical priority pathogen”, one of 12 families of bacteria that pose the greatest threat to human health.
Until now, it was believed that the Adelaide Imipenemase (AIM-1) gene was only found in the South Australian capital city after being detected in clinical samples and healthcare-associated wastewater.
But a group of scientists led by UniSA microbiologist Associate Professor Rietie Venter has shown evidence of it worldwide, pinpointing its source in a harmless environmental organism present in soil, groundwater, wastewater and even in plants.
The findings have been published in the journal Microbial Genomics.
The discovery suggests that the gene has mobilised at some stage and jumped from a harmless organism to a nasty pathogen.
“It’s an opportunistic pathogen which is ubiquitous and very resilient,” says Assoc Prof Venter.
The team used innovative ways to track and characterise antimicrobial resistance, making their discovery through wastewater analysis. Their research revealed the AIM-1 gene was prevalent at many sites throughout Adelaide and South Australia, including in every wastewater sample and river water, hinting at a wider spread of the gene than originally thought.
“We then investigated the possibility of a global distribution of the AIM-1 gene. Through extensive nucleotide and protein data base searching, we discovered the gene was also present in Asia, North America and Europe.”
However, AIM-1 was predominantly found in harmless environmental organisms and has only made the jump to the pathogen P. aeruginosa in two other locations so far (Iran and Iraq).
“Genes that are ‘mobile’ jump around all the time, but the scenario described in this study is much rarer,” says Assoc Prof Venter.
“However, as microbes are a great source of antibiotics and very competitive, it is highly likely that many bacterial resistant genes evolve in unknown organisms before making their way to dangerous pathogens, especially P. aeruginosa, which shares a habitat with harmless environmental organisms.”
Assoc Prof Venter says the AIM-1 gene requires carefully monitoring.
“If we can better understand why genes jump from environmental into human pathogens, we might be able to prevent it from happening more often,” she says.