Media release
From: Cell PressFacemask can detect viral exposure from a 10-minute conversation with an infected person
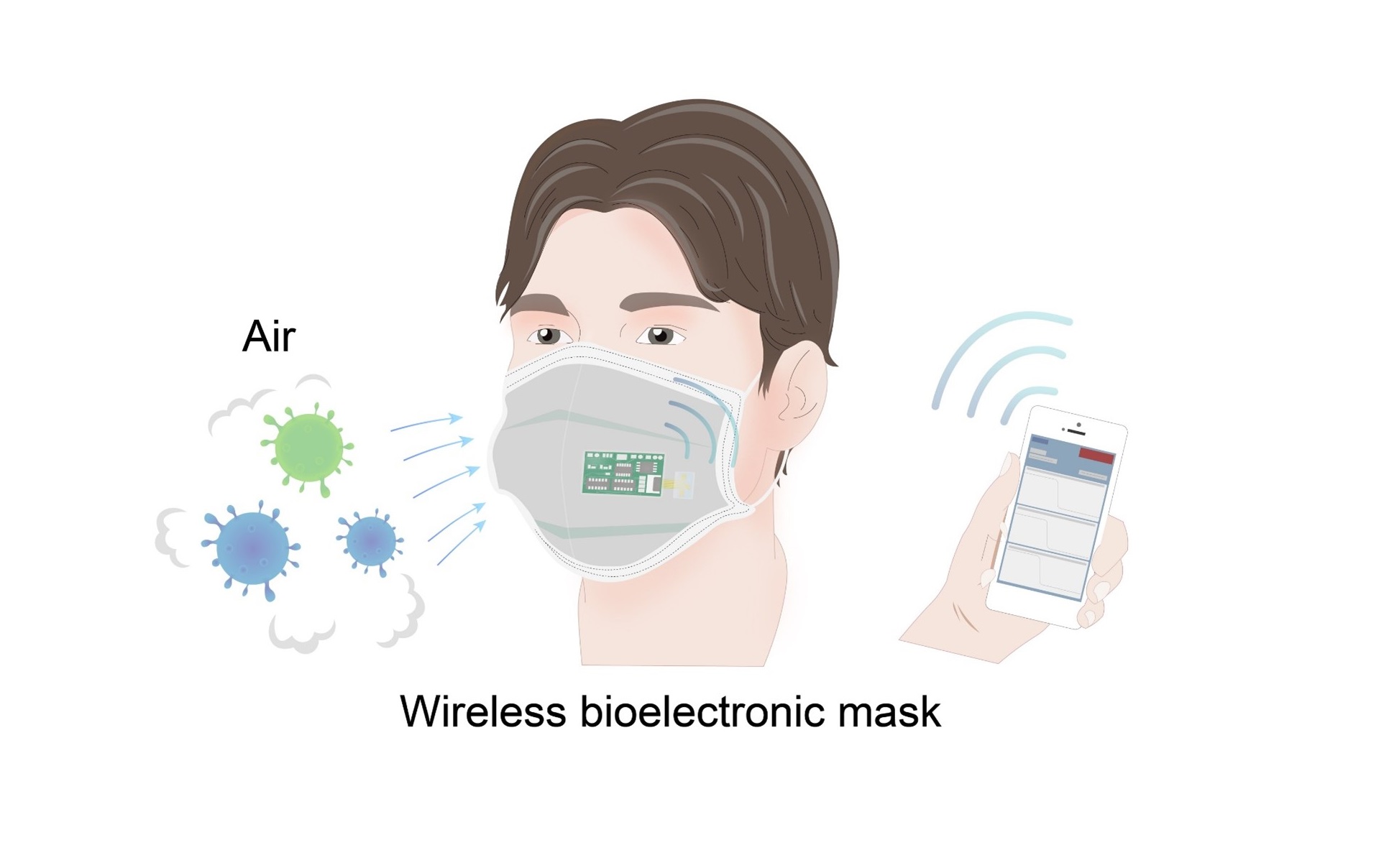
Scientists have created a face mask that can detect common respiratory viruses, including influenza and the coronavirus, in the air in droplets or aerosols. The highly sensitive mask, presented September 19 in the journal Matter, can alert the wearers via their mobile devices within 10 minutes if targeted pathogens are present in the surrounding air.
“Previous research has shown face mask wearing can reduce the risk of spreading and contracting the disease. So, we wanted to create a mask that can detect the presence of virus in the air and alert the wearer,” says Yin Fang, the study’s corresponding author and a material scientist at Shanghai Tongji University.
Respiratory pathogens that cause COVID-19 and H1N1 influenza spread through small droplets and aerosols released by infected people when they talk, cough, and sneeze. These virus-containing molecules, especially tiny aerosols, can remain suspended in the air for a long time.
Fang and his colleagues tested the mask in an enclosed chamber by spraying the viral surface protein containing trace-level liquid and aerosols on the mask. The sensor responded to as little as 0.3 microliters of liquid containing viral proteins, about 70 to 560 times less than the volume of liquid produced in one sneeze and much less than the volume produced by coughing or talking, Fang says.
The team designed a small sensor with aptamers, which are a type of synthetic molecule that can identify unique proteins of pathogens like antibodies. In their proof-of-concept design, the team modified the multi-channel sensor with three types of aptamers, which can simultaneously recognize surface proteins on SARS-CoV-2, H5N1, and H1N1.
Once the aptamers bind to the target proteins in the air, the ion-gated transistor connected will amplify the signal and alert the wearers via their phones. An ion-gated transistor is a novel type of device that is highly sensitive, and thus the mask can detect even trace levels of pathogens in the air within 10 minutes.
“Our mask would work really well in spaces with poor ventilation, such as elevators or enclosed rooms, where the risk of getting infected is high,” Fang says. In the future, if a new respiratory virus emerges, they can easily update the sensor’s design for detecting the novel pathogens, he adds.
Next, the team hopes to shorten the detection time and further increase the sensitivity of the sensor by optimizing the design of the polymers and transistors. They are also working on wearable devices for a variety of health conditions including cancers and cardiovascular diseases.
“Currently, doctors have been relying heavily on their experiences in diagnosing and treating diseases. But with richer data collected by wearable devices, disease diagnosis and treatment can become more precise,” Fang says.