-
Largest marine reptile may have been twice the length of a bus
PLOS ONE
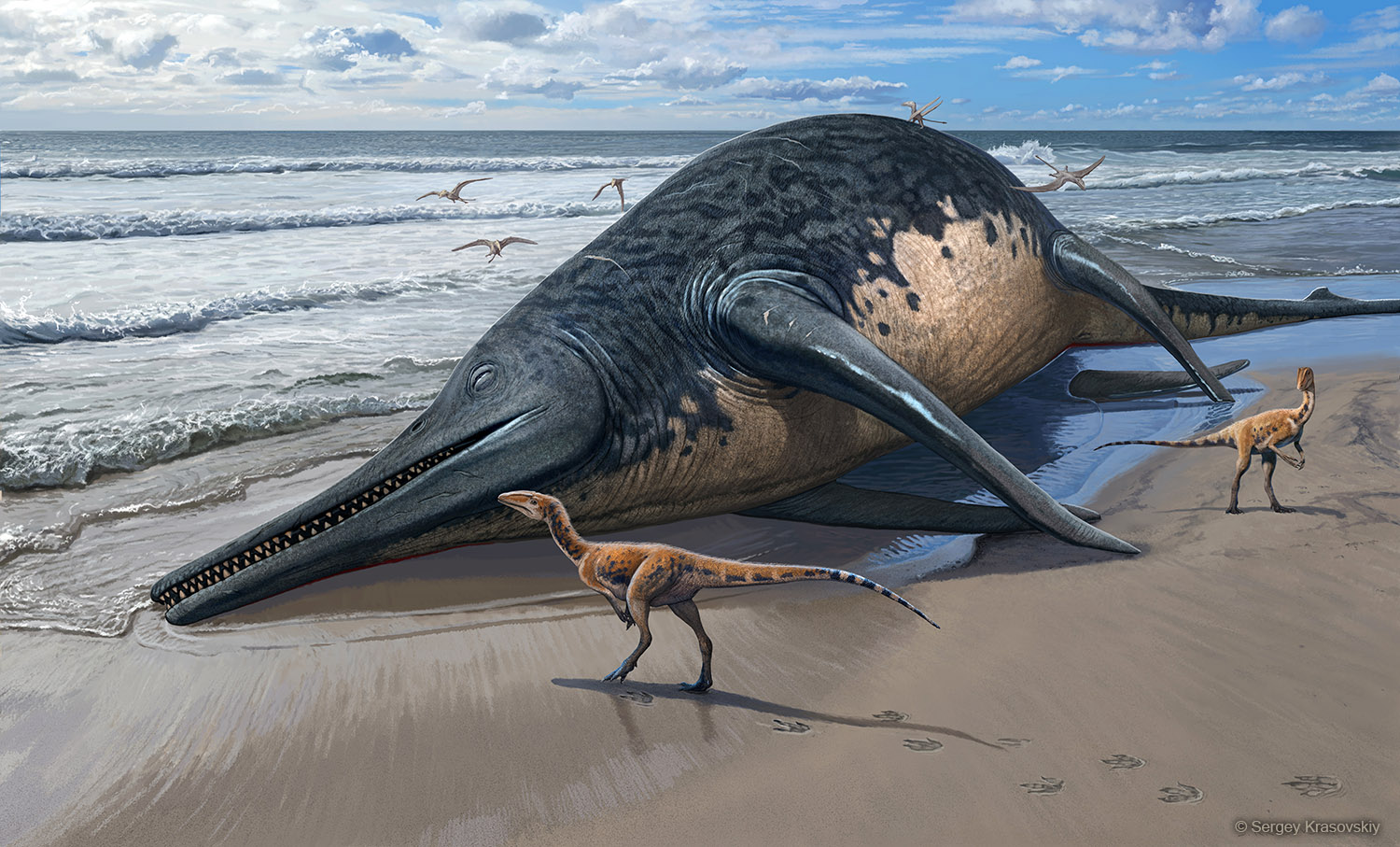
International scientists have unearthed what may be the largest marine reptile ever to be described, Ichthyotitan severnensis, at an estimated 25 metres long. The team found and pieced together fragments of an ichthyosaur jawbone found in the UK, Read more about Largest marine reptile may have been twice the length of a bus
InternationalThe University of Manchester, UK -
Is medicinal cannabis in Australia 'the wild west of medicine'?
Drug & Alcohol Review
Australian experts interviewed 17 Aussie doctors about prescribing medicinal cannabis, and identified four factors that hinder the prescription of cannabis-based treatments. Barriers included: developing the clinical capabilities needed to prescribe, Read more about Is medicinal cannabis in Australia 'the wild west of medicine'?
Australia; VIC; QLDMonash University -
Sharing needles common among injecting drug users, even those treated for hep C
Drug & Alcohol Review
Australian experts say needle and syringe sharing is common among injecting drug users who attend drug treatment clinics and needle and syringe programs. They surveyed 1,555 Aussies who had injected drugs in the past month, and found 432 (28%) had Read more about Sharing needles common among injecting drug users, even those treated for hep C
Australia; NSWKirby Institute, UNSW Sydney|National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre (NDARC)... -
Most people experiencing homelessness have mental health disorders
JAMA Psychiatry
In a meta-analysis and systematic review, Canadian researchers say that most of the people experiencing homelessness have mental health disorders, with higher prevalences than those observed in the general community. The researchers say that not Read more about Most people experiencing homelessness have mental health disorders
InternationalUniversity of Calgary, Canada -
Genetic engineering could weed out the bad things in crops
Trends in Plant Science
Danish researchers say bioengineering crops to be colourful and have differently shaped leaves could make it easier to distinguish them from weeds, making them easier to cultivate. In an opinion piece, they say introducing pigments that are already Read more about Genetic engineering could weed out the bad things in crops
InternationalUniversity of Copenhagen, Denmark -
Genetic drivers of autism could be stronger for men
JAMA Psychiatry
The degree to which genetics influence autism could be different for males and females, according to international researchers. The team analysed data from a study including over one million Swedish children, of which 12,226 received a diagnosis of Read more about Genetic drivers of autism could be stronger for men
InternationalKarolinska Institutet, Sweden -
Laser and light hair removal effectively treats excess hair growth from polycystic ovary syndrome
JAMA Dermatology
Laser and light-based therapies are effective in reducing the severity of excess hair growth in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), according to an Australian analysis of research. The team pooled together the results of six studies and Read more about Laser and light hair removal effectively treats excess hair growth from polycystic ovary syndrome
Australia; VICMonash University -
EXPERT REACTION: Climate change is set to drop the world's income by 19% and Australia will feel the pinch
Nature
Climate change is projected to reduce the income of the global economy by 19% by 2049, according to international scientists and Australia will be among the countries feeling the pinch. These economic damages are six times the costs of limiting Read more about EXPERT REACTION: Climate change is set to drop the world's income by 19% and Australia will feel the pinch
Australia; InternationalPotsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Germany -
Warming tundra's impact on carbon emissions revealed
Nature
A study published today in Nature shows the intricate relationship between climate change and carbon release in Arctic and alpine tundra ecosystems. The study, which analysed 136 datasets across 28 tundra sites, including the Silver Plains Reserve Read more about Warming tundra's impact on carbon emissions revealed
Australia; International; TASUniversity of Tasmania -
Instinct for 'fight or flight' may be much older than we thought
Nature
Our instinctive 'fight or flight' response to danger was thought to have evolved along with the sympathetic nervous system in backboned animals with a jaw, but US and Czech scientists say its origins may be much older than that. The sympathetic Read more about Instinct for 'fight or flight' may be much older than we thought
InternationalCalifornia Institute of Technology, USA, Goethe-Universität, Germany -
Injuries landing many Aussie kids and teens in hospital
This media release contains information some readers may find distressing as it refers to data about self-harm. If you or anyone you know needs help, support is available now. Call Lifeline (Aus) on 131 114 or Beyond Blue on 1300 22 4636, or Read more about Injuries landing many Aussie kids and teens in hospital
AustraliaAustralian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) -
Breaking the chains: dismantling the illegal parrot trade
DNA databases are often used by police to place criminals at the scene of a crime, but scientists from The Australian National University (ANU) in collaboration with King’s Forensics in the UK are using cutting edge, low-cost genomic sequencing Read more about Breaking the chains: dismantling the illegal parrot trade
Australia; Pacific; International; ACTThe Australian National University -
EXPERT REACTION: Worst summer on record for the Great Barrier Reef
The Reef Snapshot: Summer 2023-24 has been released today, and it highlights some of the effects of the climate driven impacts across the Great Barrier Reef. The report notes widespread coral bleaching, two cyclones and several severe flood events. Read more about EXPERT REACTION: Worst summer on record for the Great Barrier Reef
Australia; NSW; QLD; WA; TAS; ACTAustralian Science Media Centre -
Increased monitoring capacity of deadly prion diseases
A state-of-the-art service based at The Florey is increasing its capacity to protect the public from the fatal brain condition Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). The rare neurodegenerative illness, caused by misfolded proteins called prions in the Read more about Increased monitoring capacity of deadly prion diseases
Australia; VICFlorey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health -
Climate change is wiping out rare bacteria in a 'greening' Antarctica
Conservation Biology
A warming climate in Antarctica is leading to a shift in the balance of the ecosystem’s microbes which in turn could accelerate the warming climate. Plenty is known about the existential threat of climate change to plants and animals. But by Read more about Climate change is wiping out rare bacteria in a 'greening' Antarctica
Australia; NSWThe University of New South Wales -
Could motherhood and a TED-talk help bring our increasingly divided world together?
Royal Society Open Science
Humans seem more divided than ever, but international scientists say we could help bring people together by focusing on common life events such as motherhood, and recognising common ancestry. The researchers found that US mothers were more "fused" Read more about Could motherhood and a TED-talk help bring our increasingly divided world together?
InternationalUniversity of Oxford, UK -
No evidence that Tassie devil facial cancer threat has eased, scientists argue
Royal Society Open Science
In 2020, an international study was published that claimed devil facial tumour 1 (DFT1) - a transmissible cancer that has proved devastating for the charismatic critters - had shifted from being an emerging condition to an endemic disease, reducing Read more about No evidence that Tassie devil facial cancer threat has eased, scientists argue
Australia; International; TASUniversity of Cambridge, UK -
Artificial light and warmer water could increase the pressure on our kelp forests from hungry sea urchins
Proceedings of the Royal Society B
Artificial light at night and ocean warming could increase the grazing of sea urchins on kelp forests, putting pressure on these important marine habitats, say Australian researchers. Kelp forests are important habitats that provide food and shelter Read more about Artificial light and warmer water could increase the pressure on our kelp forests from hungry sea urchins
Australia; NSWThe University of New South Wales|The University of Sydney -
Fairy-wrens are more likely to help a mate in the harsh of winter
Proceedings of the Royal Society B
Superb fairy-wrens are more cooperative during winter and are more likely to respond to calls of distress from other birds when the weather is at its harshest, according to Australian research. Superb fairy-wrens are social songbirds who live in Read more about Fairy-wrens are more likely to help a mate in the harsh of winter
Australia; VIC; ACTMonash University|The Australian National University... -
Teen internet addicts who don't sleep or exercise enough more likely to miss school
Archives of Disease in Childhood
Teens who compulsively spend too much time online and don't get enough sleep or exercise are more likely to skip school or miss classes because of illness, with girls affected by internet 'addiction' more than boys, say Finnish researchers. They Read more about Teen internet addicts who don't sleep or exercise enough more likely to miss school
InternationalWestern Uusimaa Wellbeing Services County, Finland, Åbo Akademi University, Finland -
What motivates someone to manipulate their partner's reproductive choices?
PLOS ONE
Reproductive coercion and abuse - using abusive tactics to manipulate a partner's reproductive choices - may often but not always be driven by a wider pattern of coercive control, according to a small Australian study. The team conducted in-depth Read more about What motivates someone to manipulate their partner's reproductive choices?
Australia; VICThe University of Melbourne -
EXPERT REACTION: COVID-19 vaccines likely prevented nearly 18,000 deaths in NSW's early Omicron era
PLOS ONE
Australia's COVID-19 vaccination campaign likely prevented 17,760 deaths in NSW over-50s between August 2021 and July 2022, according to Australian research based on computer simulations. The team used a simulation of NSW's vaccination and COVID-19 Read more about EXPERT REACTION: COVID-19 vaccines likely prevented nearly 18,000 deaths in NSW's early Omicron era
Australia; NSW; VIC; QLDRMIT University|Monash University -
Could your sweat one day charge your fitness tracker?
Device
Your fitness tracker could one day be powered by your own sweat, according to Australian researchers who have developed tiny, sweat-powered nanogenerators that can be stored in clothing. The team say their hydroelectric nanogenerators, which they Read more about Could your sweat one day charge your fitness tracker?
Australia; NSW; VICDeakin University|Monash University|The University of New South Wales -
Bacteria behind meningitis in babies explained
eLife
Australian researchers have identified the types of E. coli responsible for neonatal meningitis – around 50 per cent of infections are caused by two types of E. coli. The study was the largest to date, examining genomes of E. coli bacteria across Read more about Bacteria behind meningitis in babies explained
Australia; QLDThe University of Queensland|Institute for Molecular Bioscience -
There is a mishmash of water theft laws and penalties across the Murray Darling Basin
Nature Water
Australian researchers have explored the mishmash of water theft laws and penalties that exist across the Murray Darling Basin states and territories and have found that there is a lack of consistency which is driving poor regulatory outcomes and Read more about There is a mishmash of water theft laws and penalties across the Murray Darling Basin
Australia; NSW; VIC; QLD; SAThe University of Adelaide -
Last whistle: Tackling tough issues athletes faced when they retire from sport
Frontiers in Psychology
Life changes radically and can be rough on athletes who are forced to retire, and a new study has found women and younger people are more prone to experience symptoms of anxiety than more mature sportsmen. Flinders University researchers surveyed Read more about Last whistle: Tackling tough issues athletes faced when they retire from sport
Australia; SAFlinders University -
How do Australia's desert animals avoid inbreeding during dry spells?
PNAS
Australia's desert-dwelling animals have vastly different ways of surviving the harsh conditions from generation to generation, according to Australian researchers. The team monitored two species - the sandy inland mouse and the lesser hairy-footed Read more about How do Australia's desert animals avoid inbreeding during dry spells?
Australia; NSW; ACTUniversity of Canberra|The University of Sydney -
Program aims to break down dementia stigma in Chinese Australian communities
Stigma about dementia is deterring Chinese Australians from seeking early diagnosis and support. University of Sydney researchers are working with the Chinese community to change that. A team of researchers is encouraging Chinese Australians to Read more about Program aims to break down dementia stigma in Chinese Australian communities
Australia; NSWThe University of Sydney -
Food and fibre sector boost needed to support NZ’s ageing population
With an ageing population placing increased strain on New Zealand’s public services, the country must earn more to maintain current living standards in the years ahead, a new discussion paper has found. The just-released paper calls for Read more about Food and fibre sector boost needed to support NZ’s ageing population
New ZealandNew Zealand Institute of Economic Research; Helen Clark Foundation -
Australian media need generative AI policies to help navigate misinformation and disinformation
Digital Journalism
New research into generative AI images shows only over a third of media organisations surveyed at the time of research have an image-specific AI policy in place. New research into generative AI images shows only over a third of media organisations Read more about Australian media need generative AI policies to help navigate misinformation and disinformation
Australia; International; VIC; QLDRMIT University|Queensland University of Technology (QUT)... -
Climate change is putting NZ’s own alpine grasshoppers at risk
Diversity and Distributions
The North Island is home to just one species of alpine grasshopper, known as Sigaus piliferus. Researchers found there are two sub-groups that adapted to different local conditions across the North Island. The two “ecotypes” are likely to Read more about Climate change is putting NZ’s own alpine grasshoppers at risk
New ZealandMassey University -
'Global blunder': Many people with breast cancer 'systematically left behind'
The Lancet
Breast cancer is now the world’s most common cancer; at the end of 2020, 7. 8 million women had been diagnosed in the past five years but survived, and in the same year, 685,000 women died from the disease. Despite improvements in research, Read more about 'Global blunder': Many people with breast cancer 'systematically left behind'
Australia; VICPeter MacCallum Cancer Centre|The University of Melbourne... -
The brain's reward system works to make others happy, not just ourselves
JNeurosci
The reward system in our brains can help us make others happy as well as making ourselves happy, according to international research. Forty-six participants were put through a challenge that involved rating their food preferences, observing others' Read more about The brain's reward system works to make others happy, not just ourselves
InternationalLudwig Maximilian University Munich, Germany -
New drug may slow rapid progression of Parkinson's disease
Nature Medicine
A drug called prasinezumab may slow signs of motor deterioration in people with rapidly progressing Parkinson’s Disease, according to an re-analysis of data from a large clinical trial by international researchers. The drug is designed to bind to Read more about New drug may slow rapid progression of Parkinson's disease
InternationalRoche Innovation Center Basel, Switzerland -
Cold killer events may be on the rise in our warming oceans
Nature Climate Change
Weirdly, global warming may actually be increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme cold events in our oceans, according to Australian research. Climate change shifts ocean currents and pressure systems, and the researchers found that changes Read more about Cold killer events may be on the rise in our warming oceans
Australia; NSW; QLDJames Cook University|NSW Government|University of the Sunshine Coast... -
Legalising weed likely doesn't lead more teens to it
JAMA Pediatrics
Making cannabis legal in the US doesn't appear to have an effect on adolescents' use of the drug, say US researchers. The investigation looked into survey data over ten years, and, while the legalisation may be associated with modest decreases in Read more about Legalising weed likely doesn't lead more teens to it
InternationalBoston College, USA -
Pregnancy complications can put women at an increased risk of early death for the next 40 years
JAMA Internal Medicine
Women who had pregnancy complications, including gestational diabetes, preterm delivery, high blood pressure, preeclampsia and having a small birthweight baby, may have an increased risk of dying prematurely that lasts for over 40 years. The research Read more about Pregnancy complications can put women at an increased risk of early death for the next 40 years
InternationalThe University of Texas, USA -
Hot weather may put more pressure on mental health services in emergency departments
Medical Journal of Australia
Hot weather could put pressure on the mental health services of emergency departments, with Australian researchers finding that women are more likely to visit an ED for mental health issues when temperatures are high. The study showed that while Read more about Hot weather may put more pressure on mental health services in emergency departments
Australia; NSWThe University of Sydney|The University of New South Wales... -
New way found to treat early relapse in leukaemia
Journal of Clinical Oncology
Researchers at Peter Mac have found a new way to treat a form of leukaemia that stops the disease in its tracks to prolong remission. New research, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, has shown how a new combination of a molecular Read more about New way found to treat early relapse in leukaemia
Australia; International; VIC; SAPeter MacCallum Cancer Centre|The University of Adelaide... -
Targeted liver cancer treatment kills cancer cells and could cut chemo side effects
International Journal of Pharmaceutics
Drug-loaded 3D printed films could change cancer treatments forever as research from the University of South Australia shows that new films not only kill more than 80% of liver cancer cells but could also significantly reduce recurrence rates Read more about Targeted liver cancer treatment kills cancer cells and could cut chemo side effects
Australia; International; SAUniversity of South Australia|The University of Adelaide -
Giant rogue waves: Southern Ocean expedition reveals wind as key cause
Physical Review Letters
A University of Melbourne expedition to the southernmost waters encircling Antarctica has discovered that wind drives the formation of colossal rogue waves, and that these unpredictable waves occur more frequently than scientists had previously Read more about Giant rogue waves: Southern Ocean expedition reveals wind as key cause
Australia; International; VICThe University of Melbourne|Swinburne University of Technology -
Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
Nature Communications
An experiment has demonstrated how networks can be leveraged to combat disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communications. The international effort led by researchers from Griffith University’s Centre for Quantum Dynamics highlights the potential of Read more about Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
Australia; International; NSW; QLDGriffith University|The University of New South Wales -
Private equity purchases of Aussie healthcare grew to $4.5 billion in 2022
Medical Journal of Australia
Private equity acquisitions of Australian health care have grown over the past fifteen years, reaching $4. 5 billion in 2022, according to new data. The researchers identified a total of 75 private equity acquisitions of health care delivery assets Read more about Private equity purchases of Aussie healthcare grew to $4.5 billion in 2022
Australia; International; TASUniversity of Tasmania|Harvard University, USA -
Melbourne radio wave exposure consistent over time
Environmental Research
Environmental exposure to radio waves from wireless technology has not changed significantly in Melbourne over the last decade, a study led by scientists at the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA) finds. Environmental Read more about Melbourne radio wave exposure consistent over time
Australia; VICAustralian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA)... -
Three new giant kangaroos bound back from the past
Megataxa
Palaeontologists from Flinders University have described three unusual new species of giant fossil kangaroo from Australia and New Guinea, finding them more diverse in shape, range and hopping method than previously thought. The three new species Read more about Three new giant kangaroos bound back from the past
Australia; Pacific; NSW; SA; TAS; NTFlinders University -
Important health information missing in online food delivery menus
Public Health Nutrition
Many menu items on online food delivery services do not display important nutritional information. Researchers say current NSW menu labelling laws need to be updated and closer monitoring needed on online food delivery services. A University of Read more about Important health information missing in online food delivery menus
Australia; NSWThe University of Sydney -
AI can write you a poem and edit your video. Now, it can help you be funnier
Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces - IUI 2024 Conference
University of Sydney researchers have developed an AI application using cartoons from The New Yorker to help people be funnier. University of Sydney researchers have used an AI-assisted application to help people write cartoon captions for cartoons Read more about AI can write you a poem and edit your video. Now, it can help you be funnier
Australia; NSWThe University of Sydney -
Our fur babies come with cuddles and a side of superbugs
ESCMID Global Congress
UK and Portuguese researchers presenting at ESCMID Global Congress say our pet kits and doggos could play a big part in spreading antibiotic-resistant bacteria. They found evidence of multidrug-resistant bacteria being passed between sick cats and Read more about Our fur babies come with cuddles and a side of superbugs
InternationalUniversity of Lisbon, Portugal -
Bonobos are less chill than we thought
Current Biology
New international research has debunked the idea that bonobos are less aggressive than chimpanzees. Over the course of the study, bonobos had three times as many physical aggressions as chimpanzees. However, while male bonobos were almost Read more about Bonobos are less chill than we thought
InternationalUniversité Toulouse Capitole -
LGBTQ+ young people with childhood trauma are at higher risk of phone addiction
JAMA Network Open
Young people who are not heterosexual or don't conform to gender norms are more likely to have childhood trauma, which in turn increases their risk of phone addiction, according to Chinese research. The team investigated the links between queer or Read more about LGBTQ+ young people with childhood trauma are at higher risk of phone addiction
InternationalSun Yat-sen University, China