-
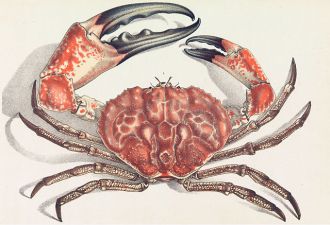
Largest crab claw ever found near Taranaki
New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics
Are ya feeling it now, Mr. Krabs? Researchers from the Netherlands are, after describing a fossil crab that boasts the largest (fossilised) crab claw ever, discovered on Waitoetoe beach in New Zealand by a local fossicker. The new species may be a Read more about Largest crab claw ever found near Taranaki
New ZealandUtrecht University, Llorenç de Villalonga -
Cutting-edge tracking technology proves Australian whale shark tourism leads the world
Journal of Sustainable Tourism
Using technology akin to a ‘fitbit’ for sharks, a team of researchers has tagged and tracked whale sharks to study the effects of tourism at Ningaloo Reef in Western Australia for the first time. In a resounding endorsement of local tourism Read more about Cutting-edge tracking technology proves Australian whale shark tourism leads the world
Australia; QLD; WAMurdoch University|The University of Queensland|University of the Sunshine Coast -
Resistance to social robots futile
Technological Forecasting and Social Change
While the rise of artificial intelligence is proving to be a contentious issue, new research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has found that the use of social robots in a commercial setting would likely be met with less resistance. Resistance to Read more about Resistance to social robots futile
Australia; WAEdith Cowan University -
Silver tourism an avenue for industry growth
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management
There is a significant opportunity to take advantage of the untapped market of silver tourism, paving the way to not only grow the economy but also offer an ever-increasing ageing population the opportunity to maintain quality of life. Silver Read more about Silver tourism an avenue for industry growth
Australia; WAEdith Cowan University|Curtin University -
Livestock guardian dogs safeguarding livelihoods and biodiversity
Ecological Solutions and Evidence
A landmark study has revealed how Livestock Guardian Dogs (LGDs) are changing predator behaviour and supporting conservation efforts in the process. A landmark study has revealed how Livestock Guardian Dogs (LGDs) are changing predator behaviour and Read more about Livestock guardian dogs safeguarding livelihoods and biodiversity
Australia; VIC; TASUniversity of Tasmania|The University of Melbourne... -
BRIEFING ALERT: Making sense of summer's weird weather, and what's coming next
This summer, the weather has had many of us scratching our heads. The idea that El Niño = hot and dry seems to have gone out the window, as rain lashed the east coast. But if you are struggling to sort your ENSO and Indian Ocean Dipole from your Read more about BRIEFING ALERT: Making sense of summer's weird weather, and what's coming next
Australia; VIC; ACTAustralian Science Media Centre|The University of Melbourne... -
Culturally diverse boards the key to sustainability
Sustainability
Research has revealed the positive impact culturally diverse boards have on the sustainability practices of Australia’s largest companies. However, the study also provides a word of caution on the ability of powerful CEOs to negate this influence. Read more about Culturally diverse boards the key to sustainability
Australia; WAMurdoch University -
Kangaroos and drag queens help an Aussie scientist win the global 'Dance your PhD' competition
Science
The global 'Dance your PhD' competition has been won by an Aussie researcher, who brought all different types of dancers together to help explain his research on eastern grey kangaroos. The video, which includes babies, drag queens, ballroom and Read more about Kangaroos and drag queens help an Aussie scientist win the global 'Dance your PhD' competition
Australia; ACTThe Australian National University -
Silence broken on gender pay gaps but we must hold organisations to account
The exposure of the gender pay gaps in large Australian organisations is a turning point for gender equality, but more must be done to hold employers to account, says a University of South Australia researcher. The exposure of the gender pay gaps Read more about Silence broken on gender pay gaps but we must hold organisations to account
Australia; SAUniversity of South Australia -
Protecting South Australian first responders against mental health impacts
Research shows emergency service personnel are twice as likely to develop anxiety, depression, and PTSD but a new Flinders University support program is aiming to prevent the onset of mental health conditions for first responders. Flinders Read more about Protecting South Australian first responders against mental health impacts
Australia; SAFlinders University
Submit to Scimex
Upcoming events
- International Fire Behaviour and Fuels Conference Bushfires present an increasing challenge to humanity and the ecosystems and atmosphere we depend on....
- Zero alcohol beverages: Are they “normalising everything about alcohol" for adolescents? Zero-alcohol drinks - drinks that contain no or very low amounts of alcohol but resemble...