-
Antidepressant use lower for mums who have grandparent support
Population Studies
Mums are less likely to take antidepressants if their own parents and parents-in-law are healthy and live close by, according to international researchers. The team tracked Finnish 488,000 mums for 14 years and also found antidepressant use was Read more about Antidepressant use lower for mums who have grandparent support
InternationalUniversity of Helsinki, Finland -
Our cultural upbringing changes how we read others' emotional facial expressions
Frontiers in Psychology
Different cultures may interpret different emotions from the same facial expression, according to international research. The team measured the brain activity of two groups of people - a group of US residents born and raised in China and a group of Read more about Our cultural upbringing changes how we read others' emotional facial expressions
InternationalUniversity of North Carolina, USA -
Planned burn-offs help avoid wildfires, but could expose more to smoke
Earth's Future
California's skies have turned orange and black several times in recent years due to smoke from major wildfires, and now authorities want to use scheduled fires to reduce the amount of fuel available for wildfires. However, new research suggests Read more about Planned burn-offs help avoid wildfires, but could expose more to smoke
InternationalCalifornia Department of Public Health, USA -
This is Perth’s perfect verge – and it comes with huge social and environmental benefits
Urban Forestry & Urban Greening
Environmental researchers have surveyed almost 1,000 Perth residents to identify what the perfect Perth verge looks like, as part of a project looking at how we can improve urban greening. “The land along streets and roads can make up more than 30% Read more about This is Perth’s perfect verge – and it comes with huge social and environmental benefits
Australia; VIC; WAMurdoch University|The University of Melbourne -
Are companies co-opting female empowerment messages to market unnecessary health products?
The BMJ
Some health companies are using female empowerment messaging to market health screening products to women who do not have an evidence-based reason for needing them, according to Australian researchers. The researchers analysed two specific examples Read more about Are companies co-opting female empowerment messages to market unnecessary health products?
Australia; NSW; QLDThe University of Sydney|The University of Queensland -
Exercising your way out of depression
BMJ
Exercise can be a powerful tool to fight depression and should be routinely prescribed as part of treatment plans, according to University of Queensland research. Exercise can be a powerful tool to fight depression and should be routinely prescribed Read more about Exercising your way out of depression
Australia; NSW; QLDThe University of Queensland|University of the Sunshine Coast... -
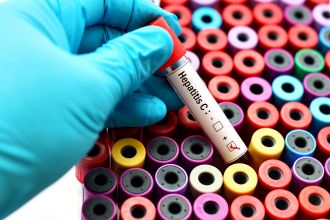
Revealing global barriers to curative hep C treatment access
Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Access to curative hepatitis C treatments depends on where you live, new research shows. Almost 90 per cent of the 57 million people living with hepatitis C live in low- and middle-income countries, but only half of these countries currently provide Read more about Revealing global barriers to curative hep C treatment access
Australia; International; NSWThe University of New South Wales|Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney -
Trapping sulfate to benefit health, industry and waterways
Nature Chemistry
Scientists have developed a new method to measure and remove sulfate from water, potentially leading to cleaner waterways and more effective nuclear waste treatments. Scientists have developed a new method to measure and remove sulfate from water, Read more about Trapping sulfate to benefit health, industry and waterways
Australia; QLDThe University of Queensland -
Revealing the gut’s crucial role in lung disease
Gut
Research led by the Centenary Institute, the University of Technology Sydney and the Hunter Medical Research Institute suggests that the gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), paving Read more about Revealing the gut’s crucial role in lung disease
Australia; NSWCentenary Institute|University of Technology Sydney (UTS)... -
EXPERT REACTION: Smokers are more likely to quit cigarettes if they switch to vapes
New England Journal of Medicine
People who are trying to quit smoking tobacco are more likely to be successful if nicotine vapes are part of their strategy, according to international research. The team recruited 1,246 would-be quitters, and assigned 622 to receive free Read more about EXPERT REACTION: Smokers are more likely to quit cigarettes if they switch to vapes
Australia; International; NSW; VICUniversity of Bern, Switzerland