-
EXPERT REACTION: Worst summer on record for the Great Barrier Reef
The Reef Snapshot: Summer 2023-24 has been released today, and it highlights some of the effects of the climate driven impacts across the Great Barrier Reef. The report notes widespread coral bleaching, two cyclones and several severe flood events. Read more about EXPERT REACTION: Worst summer on record for the Great Barrier Reef
Australia; NSW; QLD; WA; TAS; ACTAustralian Science Media Centre|Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (GBRMPA)... -
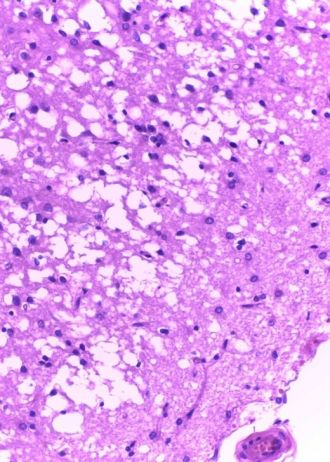
Increased monitoring capacity of deadly prion diseases
A state-of-the-art service based at The Florey is increasing its capacity to protect the public from the fatal brain condition Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). The rare neurodegenerative illness, caused by misfolded proteins called prions in the Read more about Increased monitoring capacity of deadly prion diseases
Australia; VICFlorey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health -
Climate change is wiping out rare bacteria in a 'greening' Antarctica
Conservation Biology
A warming climate in Antarctica is leading to a shift in the balance of the ecosystem’s microbes which in turn could accelerate the warming climate. Plenty is known about the existential threat of climate change to plants and animals. But by Read more about Climate change is wiping out rare bacteria in a 'greening' Antarctica
Australia; NSWThe University of New South Wales -
Could motherhood and a TED-talk help bring our increasingly divided world together?
Royal Society Open Science
Humans seem more divided than ever, but international scientists say we could help bring people together by focusing on common life events such as motherhood, and recognising common ancestry. The researchers found that US mothers were more "fused" Read more about Could motherhood and a TED-talk help bring our increasingly divided world together?
InternationalUniversity of Oxford, UK -
No evidence that Tassie devil facial cancer threat has eased, scientists argue
Royal Society Open Science
In 2020, an international study was published that claimed devil facial tumour 1 (DFT1) - a transmissible cancer that has proved devastating for the charismatic critters - had shifted from being an emerging condition to an endemic disease, reducing Read more about No evidence that Tassie devil facial cancer threat has eased, scientists argue
Australia; International; TASUniversity of Cambridge, UK -
Artificial light and warmer water could increase the pressure on our kelp forests from hungry sea urchins
Proceedings of the Royal Society B
Artificial light at night and ocean warming could increase the grazing of sea urchins on kelp forests, putting pressure on these important marine habitats, say Australian researchers. Kelp forests are important habitats that provide food and shelter Read more about Artificial light and warmer water could increase the pressure on our kelp forests from hungry sea urchins
Australia; NSWThe University of New South Wales|The University of Sydney -
Fairy-wrens are more likely to help a mate in the harsh of winter
Proceedings of the Royal Society B
Superb fairy-wrens are more cooperative during winter and are more likely to respond to calls of distress from other birds when the weather is at its harshest, according to Australian research. Superb fairy-wrens are social songbirds who live in Read more about Fairy-wrens are more likely to help a mate in the harsh of winter
Australia; VIC; ACTMonash University|The Australian National University... -
Teen internet addicts who don't sleep or exercise enough more likely to miss school
Archives of Disease in Childhood
Teens who compulsively spend too much time online and don't get enough sleep or exercise are more likely to skip school or miss classes because of illness, with girls affected by internet 'addiction' more than boys, say Finnish researchers. They Read more about Teen internet addicts who don't sleep or exercise enough more likely to miss school
InternationalWestern Uusimaa Wellbeing Services County, Finland, Åbo Akademi University, Finland -
What motivates someone to manipulate their partner's reproductive choices?
PLOS ONE
Reproductive coercion and abuse - using abusive tactics to manipulate a partner's reproductive choices - may often but not always be driven by a wider pattern of coercive control, according to a small Australian study. The team conducted in-depth Read more about What motivates someone to manipulate their partner's reproductive choices?
Australia; VICThe University of Melbourne -
EXPERT REACTION: COVID-19 vaccines likely prevented nearly 18,000 deaths in NSW's early Omicron era
PLOS ONE
Australia's COVID-19 vaccination campaign likely prevented 17,760 deaths in NSW over-50s between August 2021 and July 2022, according to Australian research based on computer simulations. The team used a simulation of NSW's vaccination and COVID-19 Read more about EXPERT REACTION: COVID-19 vaccines likely prevented nearly 18,000 deaths in NSW's early Omicron era
Australia; NSW; VIC; QLDRMIT University|Monash University -
Could your sweat one day charge your fitness tracker?
Device
Your fitness tracker could one day be powered by your own sweat, according to Australian researchers who have developed tiny, sweat-powered nanogenerators that can be stored in clothing. The team say their hydroelectric nanogenerators, which they Read more about Could your sweat one day charge your fitness tracker?
Australia; NSW; VICDeakin University|Monash University|The University of New South Wales -
Bacteria behind meningitis in babies explained
eLife
Australian researchers have identified the types of E. coli responsible for neonatal meningitis – around 50 per cent of infections are caused by two types of E. coli. The study was the largest to date, examining genomes of E. coli bacteria across Read more about Bacteria behind meningitis in babies explained
Australia; QLDThe University of Queensland|Institute for Molecular Bioscience -
There is a mishmash of water theft laws and penalties across the Murray Darling Basin
Nature Water
Australian researchers have explored the mishmash of water theft laws and penalties that exist across the Murray Darling Basin states and territories and have found that there is a lack of consistency which is driving poor regulatory outcomes and Read more about There is a mishmash of water theft laws and penalties across the Murray Darling Basin
Australia; NSW; VIC; QLD; SAThe University of Adelaide -
Last whistle: Tackling tough issues athletes faced when they retire from sport
Frontiers in Psychology
Life changes radically and can be rough on athletes who are forced to retire, and a new study has found women and younger people are more prone to experience symptoms of anxiety than more mature sportsmen. Flinders University researchers surveyed Read more about Last whistle: Tackling tough issues athletes faced when they retire from sport
Australia; SAFlinders University -
How do Australia's desert animals avoid inbreeding during dry spells?
PNAS
Australia's desert-dwelling animals have vastly different ways of surviving the harsh conditions from generation to generation, according to Australian researchers. The team monitored two species - the sandy inland mouse and the lesser hairy-footed Read more about How do Australia's desert animals avoid inbreeding during dry spells?
Australia; NSW; ACTUniversity of Canberra|The University of Sydney -
Program aims to break down dementia stigma in Chinese Australian communities
Stigma about dementia is deterring Chinese Australians from seeking early diagnosis and support. University of Sydney researchers are working with the Chinese community to change that. A team of researchers is encouraging Chinese Australians to Read more about Program aims to break down dementia stigma in Chinese Australian communities
Australia; NSWThe University of Sydney -
Food and fibre sector boost needed to support NZ’s ageing population
With an ageing population placing increased strain on New Zealand’s public services, the country must earn more to maintain current living standards in the years ahead, a new discussion paper has found. The just-released paper calls for Read more about Food and fibre sector boost needed to support NZ’s ageing population
New ZealandNew Zealand Institute of Economic Research; Helen Clark Foundation -
Australian media need generative AI policies to help navigate misinformation and disinformation
Digital Journalism
New research into generative AI images shows only over a third of media organisations surveyed at the time of research have an image-specific AI policy in place. New research into generative AI images shows only over a third of media organisations Read more about Australian media need generative AI policies to help navigate misinformation and disinformation
Australia; International; VIC; QLDRMIT University|Queensland University of Technology (QUT)... -
Climate change is putting NZ’s own alpine grasshoppers at risk
Diversity and Distributions
The North Island is home to just one species of alpine grasshopper, known as Sigaus piliferus. Researchers found there are two sub-groups that adapted to different local conditions across the North Island. The two “ecotypes” are likely to Read more about Climate change is putting NZ’s own alpine grasshoppers at risk
New ZealandMassey University -
'Global blunder': Many people with breast cancer 'systematically left behind'
The Lancet
Breast cancer is now the world’s most common cancer; at the end of 2020, 7. 8 million women had been diagnosed in the past five years but survived, and in the same year, 685,000 women died from the disease. Despite improvements in research, Read more about 'Global blunder': Many people with breast cancer 'systematically left behind'
Australia; VICPeter MacCallum Cancer Centre|The University of Melbourne...